Top 10 Hydraulic Flow Control Techniques for Efficiency and Performance How?
Hydraulic flow control is vital in various industrial applications. It enhances efficiency and performance in systems that rely on hydraulic power. Effective control of fluid movement can significantly impact operational productivity.
Understanding the top techniques for hydraulic flow control can lead to better system management. Proper flow regulation can minimize energy waste. However, challenges exist. Not all techniques suit every application, and selecting the wrong method could hinder performance.
Advancements in hydraulic technology continually evolve. Yet, some strategies may remain underutilized or misunderstood. It is crucial to continually reassess your methods and embrace innovation. The journey toward optimized hydraulic flow control is ongoing and requires a commitment to improvement.
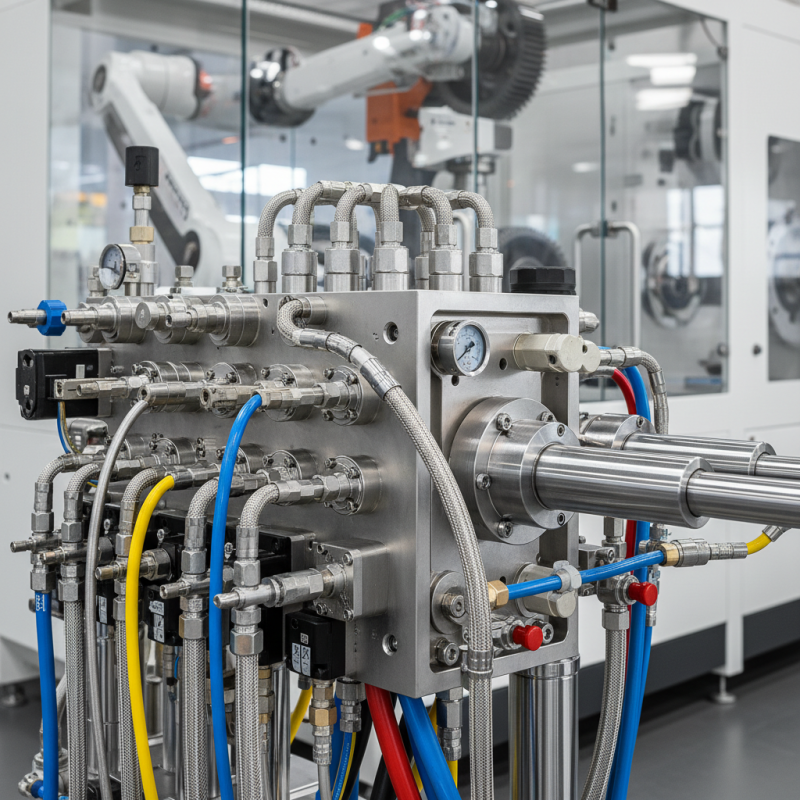
Overview of Hydraulic Flow Control in Engineering Systems
Hydraulic flow control plays a crucial role in engineering systems. It determines how fluids move and interact within machinery. Effective flow control can lead to enhanced efficiency and better performance. However, achieving this is often not straightforward. Engineers must consider various factors that influence hydraulic systems.
Different techniques are used in hydraulic flow control. These range from valves to variable speed pumps. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses. For instance, while a simple valve can regulate flow, it may not be the most efficient choice for complex systems. Sometimes, a combination of techniques is necessary to address specific challenges.
Designing an effective hydraulic system requires careful thought. Engineers often face trade-offs between efficiency and cost. Decisions made early in the design process can have long-lasting effects. Poor choices can lead to issues that are hard to fix later. Therefore, ongoing evaluation and adjustment are essential in making hydraulic systems work effectively. These challenges remind engineers that there is always room for improvement.
Fundamental Principles of Hydraulic Flow Dynamics

Hydraulic flow dynamics play a crucial role in achieving efficiency and performance in various systems. Understanding the fundamental principles can enhance flow control. At the core, pressure differentials drive fluid movement. This pressure often dictates the speed and volume of flow. Controlling these elements requires careful design and monitoring.
One effective technique is utilizing directional control valves. These valves precisely manage flow paths. However, poor valve selection can lead to inefficiencies. Misplaced expectations can cause overheating or even system failures. Always consider the compatibility of the valve with the overall design.
Tips for effective flow control include regular maintenance checks. Cleaning filters and inspecting seals prevent flow disruptions. Additionally, employing flow meters helps gauge performance accurately. Such tools can identify hidden inefficiencies. Understand, however, that not every adjustment yields immediate benefits. Continuous learning and assessment are necessary for optimizing hydraulic systems. Fine-tuning flow dynamics remains an ongoing challenge, often requiring a thoughtful approach.
Types of Hydraulic Flow Control Devices and Their Applications
Hydraulic flow control devices play a key role in enhancing efficiency and performance. These devices manage the flow and pressure in hydraulic systems. Popular types include flow control valves, pressure relief valves, and proportional valves. Flow control valves adjust flow rate within a system, ensuring the right amount of fluid reaches each actuator. This control can prevent equipment damage and optimize energy use.
Pressure relief valves protect systems from excessive pressure. They divert fluid flow back to the reservoir when pressure exceeds a preset limit. This action helps to maintain system integrity. On the other hand, proportional valves provide variable control. They adjust according to the electrical input, allowing for precise flow and pressure management.
In practice, however, the implementation of these devices isn’t always perfect. Sometimes, they don't interact seamlessly with other components. This can lead to inefficiencies. Regular maintenance is essential, yet often overlooked. Users must reflect on their systems’ performance to identify potential pitfalls and enhance overall functionality.
Top 10 Hydraulic Flow Control Techniques for Efficiency and Performance
| Technique | Type of Device | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Restrictors | Mechanical Device | Industrial Machinery | Simple design, low cost |
| Flow Control Valves | Valve System | Robotic Applications | Precise control over flow |
| Pressure Compensated Flow Control | Compensated Valve | Cylinders and Actuators | Maintains constant flow despite pressure changes |
| Variable Displacement Pumps | Pump | Construction Equipment | Adjustable flow rates enhance efficiency |
| Proportional Control Valves | Electronic Valve | Mobile Equipment | Smooth control and high responsiveness |
| Flow Meters | Measuring Device | Process Industries | Accurate flow measurement enhances monitoring |
| Hydraulic Accumulators | Storage Device | Energy Storage Systems | Store energy for peak demand times |
| Throttle Valves | Control Valve | Hydraulic Circuit | Simple, cost-effective flow adjustment |
| Flow-Rate Limiting Devices | Limiter | Agricultural Equipment | Prevents system overloads |
Techniques to Optimize Hydraulic Flow for Energy Efficiency
Optimizing hydraulic flow is crucial for improved energy efficiency in various industries. Studies reveal that improper flow can lead to energy losses up to 30%. This discrepancy stresses the importance of adopting effective control techniques. For instance, using variable displacement pumps can adjust flow according to demand, enhancing overall system performance. Reports show that systems utilizing variable displacement pumps observe a 20% increase in energy efficiency.
Moreover, implementing Pressure Compensation Techniques can stabilize flow rates. This approach mitigates excessive pressure spikes that waste energy. Research indicates that optimizing pump control can reduce energy consumption by 15%. However, many systems still underutilize these strategies. Maintenance issues often lead to declining performance. Hydraulic systems also tend to accumulate debris, which can hinder flow. Regular maintenance, coupled with flow monitoring technologies, increases reliability.
Additionally, utilizing advanced simulation tools helps in understanding hydraulic behavior under various conditions. These tools can identify inefficiencies, prompting necessary adjustments. There is still a gap in fully employing these technologies in daily operations. Continuous education and training on hydraulic systems are essential. Improving knowledge can lead to better decision-making and system upgrades, pushing for higher standards in energy efficiency.
Future Trends in Hydraulic Flow Control Technologies and Innovations
The future of hydraulic flow control is dynamic and exciting. Innovations are happening at a rapid pace. These advancements promise greater efficiency and performance. Smart systems are emerging, integrating IoT technologies. Sensors and data analytics will enhance system responsiveness. This shift could lead to real-time adjustments and improved efficiency.
Tips: Consider your specific application when choosing technology. Each system addresses unique needs. Do extensive research before making decisions.
Another trend to watch is the use of renewable energy sources. These power options can lead to greener systems. Hydraulic systems may become more eco-friendly. However, integrating renewables can pose challenges. Adaption and innovation will be crucial for success.
Tips: Regularly evaluate your current systems. Look for opportunities to enhance performance. Stay informed about new technologies and practices. This can help you remain competitive in the industry.
Related Posts
-

7 Essential Tips for Effective Hydraulic Flow Control in Your System
-

How to Select the Right Hydraulic Pressure Relief Valve for Your System Needs
-
Why Hydraulic Flow Control Valves Are Essential for Optimal Machinery Performance
-

Addressing Common Hydraulic Flow Control Challenges: Insights and Data from Industry Experts
-

7 Essential Tips for Maximizing the Life of Your Continental Hydraulic Pump
-

How to Optimize Hydraulic Flow Control for Maximum Efficiency
 skip to Main Content
skip to Main Content
