Exploring the Synergy of Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems in Modern Industrial Applications
In today's rapidly advancing industrial landscape, the integration of pneumatic and hydraulic systems has emerged as a crucial factor for enhancing efficiency and performance. Both systems serve distinct yet complementary roles, leveraging air and fluid power to perform a variety of tasks in machinery and automation. This synergy not only improves operational capabilities but also offers significant advantages in terms of energy efficiency, precision control, and responsiveness.
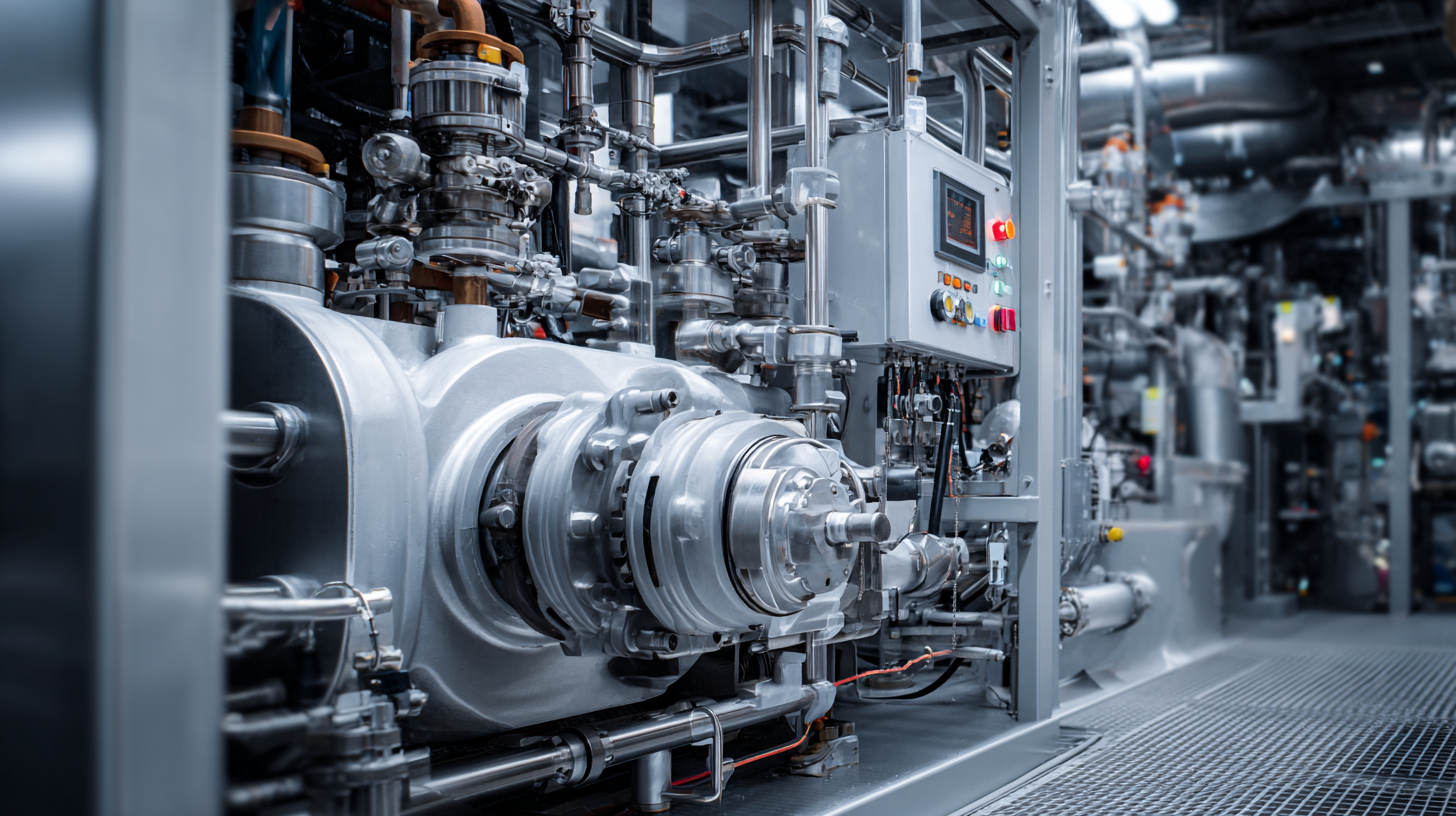

By exploring innovative ways to combine pneumatic and hydraulic technologies, industries can optimize their processes, reduce downtime, and achieve higher productivity levels. The goal of this article is to delve into the harmonization of these systems, offering practical tips and insights on how to effectively implement and benefit from their combined strengths in modern industrial applications.
Understanding the Basics of Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems in Industry
In modern industrial settings, pneumatic and hydraulic systems play a crucial role in automating processes and enhancing operational efficiency. Pneumatic systems use compressed air to transmit and control energy, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid movement and high-speed operations. They are commonly found in tools such as drills, conveyors, and actuators, where lightweight and quick-response mechanisms are essential. On the other hand, hydraulic systems utilize incompressible fluid, typically oil, to generate force and power heavy machinery. This makes them suitable for applications that demand high force output, such as in construction equipment and manufacturing presses.
Tip: When working with pneumatic systems, it’s important to regularly check for leaks to improve efficiency and reduce energy costs. In hydraulic systems, ensure that fluid levels are maintained and that the system is frequently inspected for any signs of wear, as this can prevent costly breakdowns.
Both systems have their unique advantages and are often used in tandem within various applications. Understanding the basics of each system is vital for optimizing their use; pneumatic systems excel in speed and lightness, while hydraulic systems outshine in strength and control. Mastering these fundamentals allows engineers and technicians to make informed choices that enhance productivity and operational safety in industrial environments.
Identifying Key Benefits of Integrating Pneumatic and Hydraulic Technologies
The integration of pneumatic and hydraulic systems presents numerous benefits for modern industrial applications, particularly in enhancing efficiency and performance across various sectors. Recent advancements in sensor technology have demonstrated significant improvements in the ability to monitor and optimize fluid power systems. For instance, machine learning models are now capable of predicting anomalies in compressed air usage, allowing for proactive leak detection and energy optimizations. This proactive approach can lead to efficiency increases of up to 20% in industrial pneumatic systems, as indicated by recent studies.

Moreover, the National Fluid Power Association highlights the continued relevance and growth of fluid power technologies, which remains strong even as electric alternatives gain traction. The positive sentiment in the fluid power industry is further evidenced by a report indicating a projected growth rate of 6% annually over the next five years. As companies seek to harness the benefits of both pneumatic and hydraulic technologies, the convergence of these systems not only enhances the adaptability and flexibility of industrial operations but also supports the ongoing transition towards smart manufacturing practices, aligning with Industry 4.0 advancements.
Evaluating Efficiency Gains Through Combined System Applications
The integration of pneumatic and hydraulic systems in industrial applications presents profound opportunities for enhancing operational efficiency. Pneumatic systems, renowned for their speed and responsiveness, complement hydraulic systems, which excel in providing substantial force and control. By strategically combining these two technologies, industries can leverage the best features of both systems, leading to improved performance in manufacturing processes.
Efficiency gains become evident when these systems operate in harmony. For instance, pneumatic actuators can quickly position tools or materials, while hydraulic systems handle heavy lifting and precise movements. This synergy not only reduces cycle times but also enhances accuracy and reliability, resulting in lower operational costs. Additionally, the dual-system approach mitigates the risk of system failure, as the redundancy of using two different power sources provides an added layer of safety and resilience in critical applications.
Efficiency Gains of Combined Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
Implementing Best Practices for Maintenance of Combined Systems
In modern industrial applications, the collaboration of pneumatic and hydraulic systems can significantly enhance operational efficiency. However, maintaining these combined systems requires a strategic approach to ensure longevity and optimal performance. According to a report by the International Fluid Power Society, proper maintenance can improve system reliability by up to 30%. This highlights the importance of implementing best practices tailored for integrated systems.
One fundamental tip is to establish a regular maintenance schedule that includes both pneumatic and hydraulic components. Inspect seals, filters, and hoses routinely to minimize leaks and pressure losses that can hinder performance. Additionally, using compatible fluids and lubricants is crucial for avoiding cross-contamination issues that can lead to system failure. A study published by the Hydraulic Institute indicates that over 40% of hydraulic failures can be traced back to improper fluid maintenance.
Another critical aspect is employee training. Ensuring that staff are well-versed in the functionality and maintenance requirements of both systems can greatly reduce downtime. Regular training programs can emphasize the significance of monitoring system pressures and temperatures, aligning with findings from the Fluid Power Educational Foundation, which noted that adequate training can lead to a 25% decrease in maintenance-related incidents. These practices not only ensure efficiency but also set a foundation for a more productive and sustainable industrial environment.
Case Studies: Successful Applications in Various Industrial Sectors
In recent years, the integration of pneumatic and hydraulic systems in industrial applications has proven to be a game-changer across various sectors. A notable case study can be found in the automotive manufacturing industry, where companies like Ford have successfully combined these two systems to enhance efficiency on assembly lines. According to a report by the International Society of Automation, the implementation of hybrid systems has reduced operational costs by up to 15%, while simultaneously improving production rates by as much as 20%. This showcases the potential of leveraging the best attributes of both pneumatic and hydraulic systems—where pneumatic systems provide speed and flexibility, and hydraulic systems offer power and precision.

Similar advancements are seen in the aerospace sector, where Boeing has utilized the synergy of pneumatic and hydraulic systems in its aircraft manufacturing processes. A recent market analysis revealed that the aerospace industry is predicted to witness a 5% growth annually in the adoption of integrated fluid power systems. By combining pneumatic drives for lighter weight operations with hydraulic systems for heavy lifting, companies have enhanced safety measures and improved overall workflow. Indeed, such collaborations not only contribute to cost savings but also bolster innovation in product designs and operational methodologies, creating a more agile manufacturing landscape.
Related Posts
-
What Are the Key Components of Hydraulics Products and Their Applications
-

5 Best Fluid Power Hydraulics Solutions for Optimal Performance
-
Why Fluid Power Hydraulics Are Essential for Modern Industry
-
Understanding the Power of Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems in Modern Industry with Over 300 Billion USD Revenue
-

Essential Checklist for Selecting the Right Hydraulic Check Valves for Your Applications
-

7 Best Pressure Reducing Valves You Should Consider for Optimal Performance
 skip to Main Content
skip to Main Content
