What Are Hydraulic Power Units and How Do They Work?
Hydraulic power units are vital in many industries, providing essential force and motion. These systems convert hydraulic energy into mechanical energy, powering various machines. According to John Smith, a hydraulic systems expert, "Hydraulic power units transform energy, enabling countless applications." His insights highlight the importance of understanding these technologies.
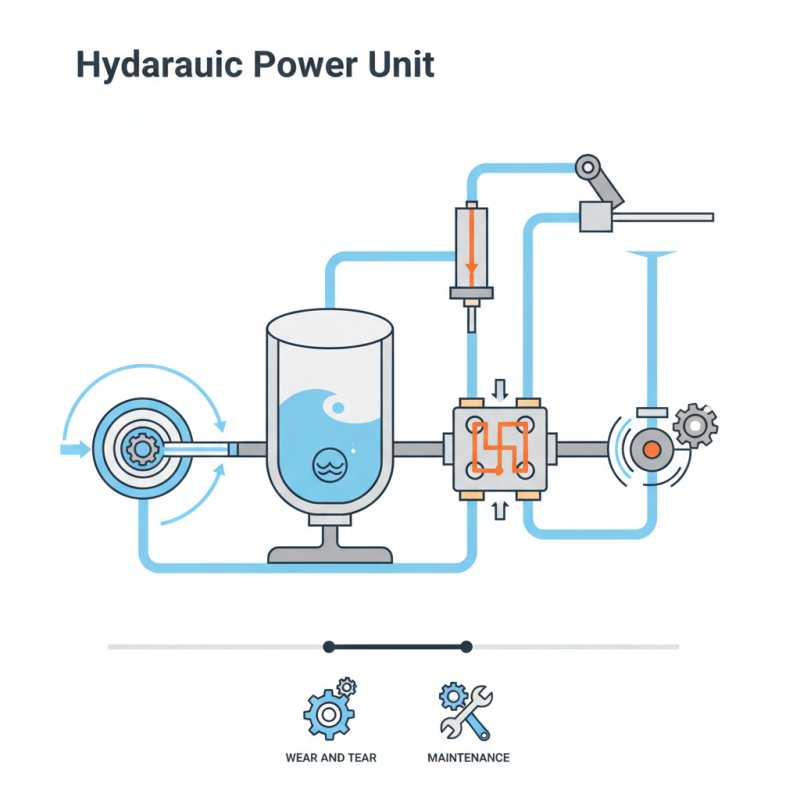
These units consist of several components: pumps, motors, valves, and tanks. Each part plays a crucial role in the system. For instance, pumps generate hydraulic fluid flow, while valves control that flow. Observing a hydraulic power unit can be complex. The intricate interplay of components often overwhelms newcomers.
Despite their efficiency, hydraulic power units require careful maintenance. Issues can arise from wear and tear. Sometimes, systems fail, prompting critical evaluations. Mistakes in understanding these units can lead to operational setbacks. Reflecting on these challenges can enhance knowledge and improve practices in the industry.
Definition of Hydraulic Power Units and Their Purpose
Hydraulic power units (HPUs) are essential systems in modern machinery. They utilize hydraulic fluid to transfer energy and operate various mechanical functions. These units convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, making them vital in fields like construction and manufacturing.
HPUs consist of several key components. A pump moves fluid through the system, creating pressure. This pressure activates cylinders or motors, leading to movement. Valves control fluid flow, ensuring the system operates smoothly. Understanding these parts helps users maintain efficiency.
**Tip:** Regular maintenance can prevent unexpected failures. Inspect hoses and connections frequently.
Additionally, HPUs require careful fluid management. Using the right hydraulic fluid is crucial. It impacts performance, efficiency, and longevity. Low-quality fluids can lead to breakdowns or leaks, which are costly.
**Tip:** Monitor fluid levels consistently. This simple practice can avoid serious issues down the line.
Choosing the correct HPU for a specific application is challenging. It's essential to analyze energy requirements and load capabilities. Inappropriate sizing may result in inefficiencies.
**Tip:** Consult with professionals for optimal system design. Their expertise can guide important decisions.
Hydraulic Power Units Performance Metrics
This bar chart represents key performance metrics of hydraulic power units, including pressure, flow rate, power, and efficiency. The data illustrates the typical values observed in hydraulic systems for optimal performance.
Components of Hydraulic Power Units and Their Functions
Hydraulic power units (HPUs) are essential devices that convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. They consist of various components, each playing a crucial role in the system. The key parts include the hydraulic pump, reservoir, motor, and valves. Each has specific functions that contribute to the overall operation.
The hydraulic pump generates fluid flow, which creates pressure. Typically, gear or piston pumps are used. The reservoir holds the hydraulic fluid, often oil, which helps manage heat and contaminants. Motors power the pump, providing the mechanical force needed for operation. Valves control the flow and direction of the fluid, ensuring that the energy is directed where it’s needed. These components need regular maintenance to function properly.
One must ponder how these units can improve efficiency. However, the complexity can lead to issues if not managed carefully. Leaks or blockages can reduce performance. Operators should remain vigilant about system integrity. It’s important to recognize that while HPUs are robust, they require attention and care. The interaction among the components is key to their success. Understanding each part helps in troubleshooting and ensuring reliability.
How Hydraulic Power Units Generate and Control Hydraulic Power

Hydraulic power units (HPUs) play a crucial role in generating and controlling hydraulic power for various applications. These systems consist of a power source, usually an electric motor or engine, a hydraulic pump, a reservoir for hydraulic fluid, and control components. The motor drives the pump, which moves fluid from the reservoir into the hydraulic system. As the fluid is pressurized, it can then perform work, such as lifting loads or powering machinery.
The control of hydraulic power is multifaceted. Users can adjust pressure settings, flow rates, and directional control through valves. This flexibility allows for precision in operations. However, designing an HPU that meets specific needs can be challenging. A system that lacks proper regulation can lead to inconsistent performance. It may not always respond as intended. Retrofitting existing units for new applications can also create complications. Balancing power output and efficiency is not a straightforward task.
Understanding how HPUs work requires attention to detail. Operators must monitor fluid levels, filter cleanliness, and overall system integrity. Neglecting these aspects can lead to failures. Additionally, evaluating the energy consumption of these units can prompt reflections on sustainability. Engaging with these systems opens avenues for innovation and improvement. Each adjustment and challenge faced can uncover new solutions for efficiency in hydraulic power applications.
Applications of Hydraulic Power Units in Various Industries
Hydraulic power units (HPUs) play a vital role across various industries. They convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, powering numerous applications. In manufacturing, HPUs are essential for controls in injection molding and metal pressing. These systems ensure precision and efficiency in production lines. According to a report by the International Hydraulics Association, the global hydraulic power market is expected to grow by 5% annually, showcasing their significance.
In the construction sector, HPUs provide reliable power for heavy equipment like excavators and cranes. They enable operators to perform demanding tasks with ease. An estimated 45% of construction machinery relies on hydraulic systems, making them a cornerstone of the industry. However, maintenance often falls short, leading to downtime. A survey revealed that 30% of machinery failures are due to hydraulic issues. Such statistics underline the importance of regular inspections and timely repairs.
Moreover, HPUs are pivotal in the automotive industry. They assist in assembly line operations, allowing efficient production of vehicles. The rise of electric vehicles also points to increasing hydraulic applications in testing and assembly processes. While this trend is promising, it also raises questions about adapting existing hydraulic technologies to new automotive innovations. Industries need to stay ahead in integrating these technologies sustainably.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Hydraulic Power Units

Maintaining hydraulic power units is crucial for their performance. Regular inspection helps identify leaks and wear. Look for signs of oil around hoses and fittings. If a hose appears frayed or cracked, it should be replaced immediately. Clean filters can significantly enhance the unit's efficiency, preventing contamination in the system.
Understanding how to troubleshoot common issues is equally important. If the hydraulic system is slow, it might indicate low fluid levels. Check the reservoir to ensure data is accurate. Unusual noises can signal air in the system or impending pump failure. Listen closely during operation. It's advisable to keep a maintenance log that tracks service intervals and anomalies. Regular documentation can reveal patterns that may need your attention.
Benches in the maintenance process can lead to problems. Skipping checks is tempting, but it could cause breakdowns. Reflect on the last time you performed a thorough inspection. Investing time in proactive maintenance saves money in the long run. Small problems can escalate if neglected. Being diligent is key to the longevity of hydraulic power units.
Related Posts
-
2026 Top Proportional Valves for Precision Control in Automation
-

7 Best Pressure Reducing Valves You Should Consider for Optimal Performance
-
Top 10 Hydraulic Flow Control Techniques for Efficiency and Performance How?
-

Top Hydraulic Parts for Enhanced Performance in Machinery?
-

Essential Checklist for Selecting the Right Hydraulic Check Valves for Your Applications
-

Why Hydraulic Continental Systems Are Essential for Modern Engineering?
 skip to Main Content
skip to Main Content
