Top 10 Benefits of Using Automated Valves in Industry
The industrial landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by the need for efficiency and safety. One significant advancement is the adoption of automated valves. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the automated valve market is projected to grow by 6.1% annually, reaching USD 7.6 billion by 2026. This growth indicates a strong industry shift toward advanced solutions.
Automated valves streamline processes across various sectors, including oil and gas, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. They enhance operational efficiency by minimizing human error and providing precise control. For instance, automated valves can reduce downtime by 15% through quicker response times and reduce the need for manual intervention.
However, reliance on technology poses challenges. Companies may face unexpected failures if their automated systems are not properly maintained. Understanding these risks is crucial for maximizing the benefits of automated valves while ensuring robust operation. Embracing this technology can yield significant advantages, but awareness of potential pitfalls is equally important.
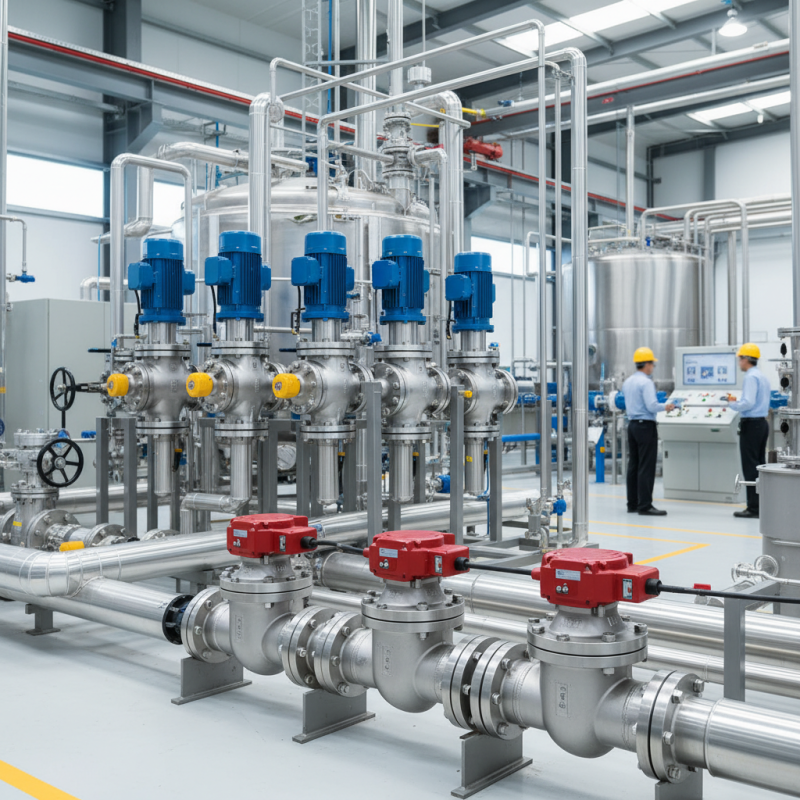

Benefits of Increased Efficiency with Automated Valves

Automated valves play a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency across various industries. According to a recent report by the International Society of Automation, companies that implement automated valves can experience a 20% increase in overall productivity. This is largely due to reduced manual intervention, allowing workers to focus on more critical tasks. Automated systems can operate continuously without breaks, minimizing downtime.
These valves also contribute to precise control of fluid dynamics. A study from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers revealed that precise valve positioning can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%. This energy efficiency translates into significant cost savings over time. However, there is a learning curve associated with integrating automated valves into existing systems. Staff may require training to fully utilize their capabilities.
While the benefits are clear, some organizations still hesitate. Concerns regarding initial investment and technology adoption often arise. Industry reports indicate that 78% of companies that delayed automation felt overwhelmed by the transition. Yet those that embraced this change saw long-term gains. The journey can be challenging, but the improvements in workflow efficiency are worth considering.
Enhancing Safety Standards in Industrial Applications
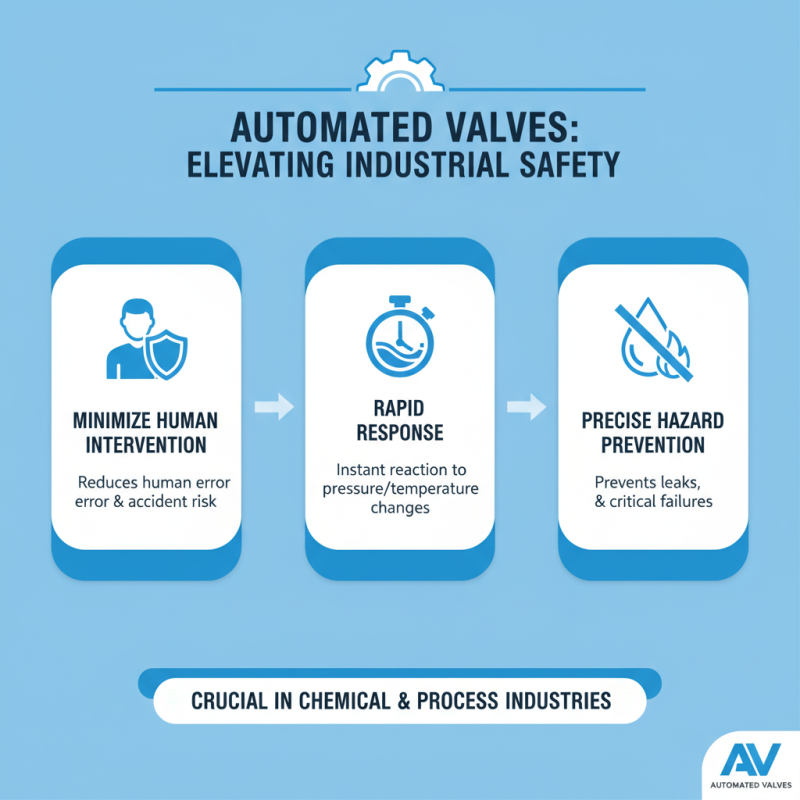
Automated valves play a crucial role in enhancing safety standards within industrial applications. These devices minimize human intervention, reducing the chances of accidents. For instance, in chemical industries, automated valves can swiftly respond to changes in pressure and temperature, averting potential hazards. This precision is vital in avoiding leaks or explosions.
Moreover, automated valves integrate advanced sensors. These sensors constantly monitor operating conditions and send alerts to operators. In some cases, immediate shut-off capabilities engage, preventing catastrophic failures. However, there can be concerns about false alarms. Operators must regularly calibrate and maintain these systems to ensure accuracy. Balancing automation with human oversight remains a challenge.
Further, while automated systems improve safety, they also introduce complexity. Training personnel to manage these systems is essential. There's a risk that workers may become overly reliant on automation. Regular drills and assessments can counteract this. By fostering a culture of safety and preparedness, industries can maximize the benefits of automation while minimizing risks.
Cost Savings Achieved Through Automation of Valves
Automated valves can lead to significant cost savings for many industries. By reducing manual labor, companies can lower their operational expenses. Maintenance costs also decrease, as automated systems often require less frequent servicing compared to manual ones. This means fewer interruptions in production. Yet, not all systems work seamlessly at first. There may be a learning curve for staff. Proper training is essential to fully capitalize on these devices.
Energy efficiency is another key advantage. Automated valves can optimize flow rates, minimizing waste. This translates to lower energy bills over time. However, initial setup costs can be a concern. Some companies might hesitate to invest upfront. It's important to run a cost-benefit analysis to weigh potential savings against installation expenses. Integration can be challenging. Existing systems might need upgrades for compatibility.
Despite these challenges, the long-term financial benefits are clearer. When valves operate efficiently, they enhance production reliability. This leads to better overall performance. As industries increasingly embrace automation, it’s crucial to analyze and refine processes. Identifying areas for improvement can lead to even greater savings. Embracing change is sometimes difficult, but the results can be rewarding.
Top 10 Benefits of Using Automated Valves in Industry
Improved Process Control and Precision in Operations
Automated valves play a crucial role in industrial settings. They enhance process control and precision in various operations. These valves allow for accurate flow regulation and pressure management, reducing human error significantly. In addition, they can respond faster than manual systems, ensuring that processes run smoothly and efficiently. This improved responsiveness can prevent costly downtime.
Tips for implementing automated valves include thorough testing before deployment. Conduct regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Understand your system's specific requirements. Not all applications need the same type of valve automation. Sometimes, manual control may offer better results in certain situations, making it important to analyze each case carefully.
Efficient communication between components is vital. Automated valves must integrate seamlessly with existing systems. However, troubleshooting can be complex. Users may need to adapt to new technology, and training is essential. A clear understanding of the automation process enhances overall effectiveness. Imagine a well-oiled machine where every part works perfectly together—this is the goal. Embrace the potential of automated valves, but remain open to improvements.
Top 10 Benefits of Using Automated Valves in Industry - Improved Process Control and Precision in Operations
| Benefit | Description | Industry Impact | Estimated Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Process Control | Automated valves offer precise control over fluid flow, leading to better process management. | Manufacturing, Oil & Gas | 20% |
| Increased Efficiency | Rapid and responsive adjustments improve overall system efficiency. | Food Processing, Chemical | 15% |
| Reduced Labor Costs | Less manual intervention reduces labor needs, cutting operational costs. | Pharmaceuticals, Water Treatment | 25% |
| Improved Safety | Automated systems minimize human error, enhancing workplace safety. | Oil & Gas, Mining | 30% |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Allows operators to monitor system performance in real time. | Utilities, HVAC | 10% |
| Higher Precision | Enables accurate control of fluid characteristics, essential for product quality. | Chemical, Aerospace | 18% |
| Lower Maintenance Needs | Fewer mechanical parts lead to less wear and tear and lower maintenance costs. | All Industries | 12% |
| Scalability | Automated systems can easily adapt to increasing production demands. | Manufacturing, Distribution | 22% |
| Energy Efficiency | Optimized flow control reduces energy usage across systems. | Process Industries | 15% |
| Data Collection | Automated valves can integrate with systems to collect operational data. | All Industries | 20% |
Reduction of Human Error in Valve Management Systems
Automated valves play a significant role in reducing human error in valve management systems. Manual operations often lead to mistakes. Operators may misjudge settings or fail to follow protocols. Automation eliminates these risks, creating a more reliable system. Each valve can operate with precision, guided by algorithms programmed to optimize performance.
Tips for training staff on automated systems are crucial. Ensure team members understand the technology. Regular workshops can foster familiarity. Encourage open discussions about potential pitfalls in automation.
Monitoring data helps identify issues before they escalate. Automated systems provide real-time feedback. However, they can still experience glitches. Continuous evaluation of system performance is vital. Don't hesitate to reassess processes when errors arise.
Related Posts
-

How to Optimize Your System with Automated Valves for Maximum Efficiency
-

12 Key Reasons Why Directional Control Valves Are Essential for Efficient Fluid Power Systems
-

What is the Future of Automated Valves in Modern Industries
-

Exploring the Future of Control Valves: Innovations and Trends Driving Efficiency in Industry
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Control Valves for Your Industrial Applications with Expert Insights
-

What is an Electric Valve? Understanding Types, Applications, and Benefits
 skip to Main Content
skip to Main Content
